Change Mon0 Channel Aircrack For Mac
Airodump-ng is used for packet capturing of raw 802.11 frames and is particularly suitable for collecting WEP IVs (Initialization Vector) for the intent of using them with aircrack-ng.If you have a GPS receiver connected to the computer, airodump-ng is capable of logging.
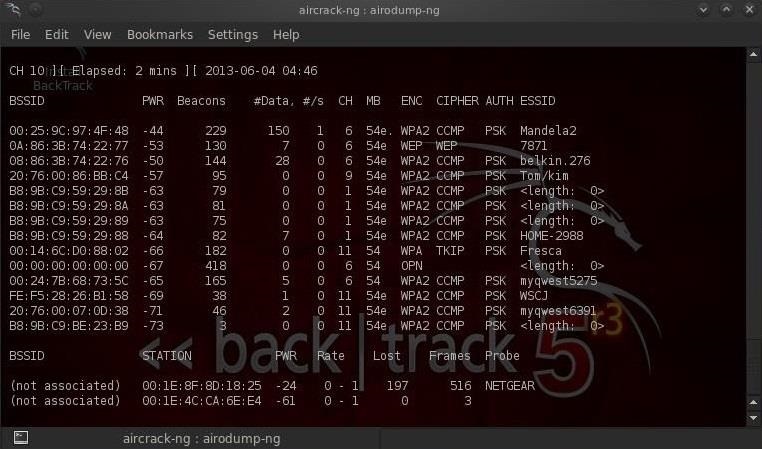
BSSID The MAC address of the AP PWR Signal strength. Some drivers don't report it Beacons Number of beacon frames received. If you don't have a signal strength you can estimate it by the number of beacons: the more beacons, the better the signal quality Data Number of data frames received CH Channel the AP is operating on MB Speed or AP Mode. 11 is pure 802.11b, 54 pure 802.11g.
Values between are a mixture ENC Encryption: OPN: no encryption, WEP: WEP encryption, WPA: WPA or WPA2 encryption, WEP?: WEP or WPA (don't know yet) ESSID The network name. Sometimes hidden. Once the packet is injected, the active client connection will be disconnected from the AP. Most of today computer will auto connect the AP because of the client system password saving function.
Aug 08, 2017 I am trying to crack wpa/wpa2 using aircrack but airdoump-ng fixed channel is changing rapidly despite of stoping network manager. Will any one help? After in arpreplay i also get this error: mon0. If you want to know how to hack WiFi access point – just read this step by step aircrack-ng tutorial, run the verified commands and hack WiFi password easily. With the help a these commands you will be able to hack WiFi AP (access points) that use WPA/WPA2-PSK (pre-shared key) encryption.
How To Install Aircrack Ng
After you done with the injection,let the packet capturing run for a while. This is important so that you capture the AP authentication information that it send to the client.How long you need to wait?? The rule of thumb that I use, you need to monitor the active packet transmission between the client and the AP. An active connection mean that the client user is actively using the connection.
How To Use Aircrack
This mean that he has successfully connected to the AP. Sony handycam software for mac. About TheGeekySpace is a site that dedicates it's mission to give the best How to's in the world of Open Source,Networking,Linux,tools and any thing related to technologies. This idea came about from it's founder during his years of working in the fields of Telecommunication/IT.TheGeekySpace mission is to help bridging the gaps between knowledge and practical by giving easy to follow tips and tricks.We hope visitors will find this site helpful in the pursue of knowledge and having fun at the same time.Don't forget to Subscribe to us!
This section provides a general overview. Not all options apply to all attacks. See the details of the specific attack for the relevant details.
Usage:
For all the attacks except deauthentication and fake authentication, you may use the following filters to limit which packets will be presented to the particular attack. The most commonly used filter option is the “-b” to select a specific access point. For typical usage, the “-b” is the only one you use.
Filter options:
- -d dmac : MAC address, Destination
- -m len : minimum packet length
- -u type : frame control, type field
- -t tods : frame control, To DS bit
- -w iswep : frame control, WEP bit
When replaying (injecting) packets, the following options apply. Keep in mind that not every option is relevant for every attack. The specific attack documentation provides examples of the relevant options.
Replay options:
- -p fctrl : set frame control word (hex)
- -c dmac : set Destination MAC address
- -e essid : For fakeauth attack or injection test, it sets target AP SSID. This is optional when the SSID is not hidden.
- -g value : change ring buffer size (default: 8)
- -l IP : set source IP in fragments
- -q sec : seconds between keep-alives (-1)
- “-B” or “–bittest” : bit rate test (Applies only to test mode)
- “-D” :disables AP detection. Some modes will not proceed if the AP beacon is not heard. This disables this functionality.
- “-F” or “–fast” : chooses first matching packet. For test mode, it just checks basic injection and skips all other tests.
- “-R” disables /dev/rtc usage. Some systems experience lockups or other problems with RTC. This disables the usage.
The attacks can obtain packets to replay from two sources. The first being a live flow of packets from your wireless card. The second being from a pcap file. Standard Pcap format (Packet CAPture, associated with the libpcap library http://www.tcpdump.org), is recognized by most commercial and open-source traffic capture and analysis tools. Reading from a file is an often overlooked feature of aireplay-ng. This allows you to read packets from other capture sessions. Keep in mind that various attacks generate pcap files for easy reuse.
How to format usb to fat32 on mac. Source options:
- -r file : extract packets from this pcap file
Ruler in microsoft 2016. This is how you specify which mode (attack) the program will operate in. Depending on the mode, not all options above are applicable.
Attack modes (Numbers can still be used):
- - -deauth count : deauthenticate 1 or all stations (-0)
- - -fakeauth delay : fake authentication with AP (-1)
- - -interactive : interactive frame selection (-2)
- - -chopchop : decrypt/chopchop WEP packet (-4)
- - -test : injection test (-9)